Research |
Climate and Health
|
The availability of on-line and real-time sources of big data sets gives us the opportunity to monitor how climate variables (among many other factors) influence the spread of Dengue, Antibiotic Resistance, and other outbreaks around the world.
|
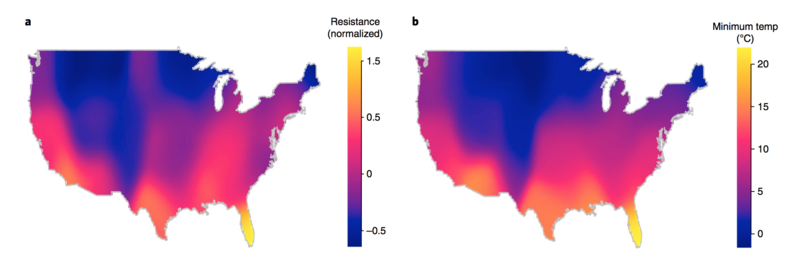
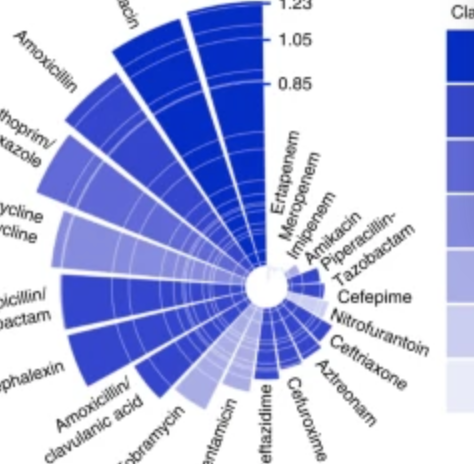
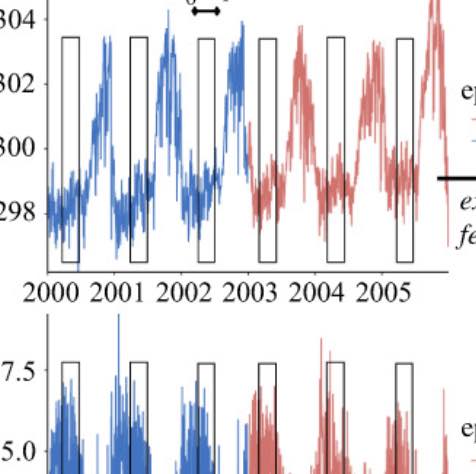
Figure. Antibiotic Resistant outbreaks across pathogens shown on the left panel and Minimum Air Temeprature on the right panel.
From: MacFadden DR, McGough SF, Fisman D, Santillana M, Brownstein JS. Antibiotic Resistance Increases with Local Temperature Nature Climate Change 8 (2018), pp 510-514. (PDF) |
Related publications
|
Antibiotic Resistance Increases with Local Temperature
MacFadden DR, McGough SF, Fisman D, Santillana M, Brownstein JS. Nature Climate Change. 2018;8 :510–514. Abstract
Bacteria that cause infections in humans can develop or acquire resistance to antibiotics commonly used against them1,2. Antimicrobial resistance (in bacteria and other microbes) causes significant morbidity worldwide, and some estimates indicate the attributable mortality could reach up to 10 million by 20502,3,4. Antibiotic resistance in bacteria is believed to develop largely under the selective pressure of antibiotic use; however, other factors may contribute to population level increases in antibiotic resistance1,2. We explored the role of climate (temperature) and additional factors on the distribution of antibiotic resistance across the United States, and here we show that increasing local temperature as well as population density are associated with increasing antibiotic resistance (percent resistant) in common pathogens. We found that an increase in temperature of 10 °C across regions was associated with an increases in antibiotic resistance of 4.2%, 2.2%, and 2.7% for the common pathogens Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus. The associations between temperature and antibiotic resistance in this ecological study are consistent across most classes of antibiotics and pathogens and may be strengthening over time. These findings suggest that current forecasts of the burden of antibiotic resistance could be significant underestimates in the face of a growing population and climate change4. |
|
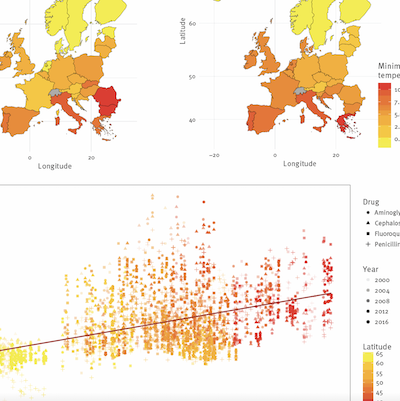
Rates of increase of antibiotic resistance and ambient temperature in Europe: a cross-national analysis of 28 countries between 2000-2016
McGough S, MacFadden DR, Hattab MW, Mølbak K, Santillana M. Eurosurveillance. 2020;25 (45) :1900414. Abstract
BackgroundThe rapid increase of bacterial antibiotic resistance could soon render our most effective method to address infections obsolete. Factors influencing pathogen resistance prevalence in human populations remain poorly described, though temperature is known to contribute to mechanisms of spread. AimTo quantify the role of temperature, spatially and temporally, as a mechanistic modulator of transmission of antibiotic resistant microbes. MethodsAn ecologic analysis was performed on country-level antibiotic resistance prevalence in three common bacterial pathogens across 28 European countries, collectively representing over 4 million tested isolates. Associations of minimum temperature and other predictors with change in antibiotic resistance rates over 17 years (2000–2016) were evaluated with multivariable models. The effects of predictors on the antibiotic resistance rate change across geographies were quantified. ResultsDuring 2000–2016, for Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae, European countries with 10°C warmer ambient minimum temperatures compared to others, experienced more rapid resistance increases across all antibiotic classes. Increases ranged between 0.33%/year (95% CI: 0.2 to 0.5) and 1.2%/year (95% CI: 0.4 to 1.9), even after accounting for recognised resistance drivers including antibiotic consumption and population density. For Staphylococcus aureus a decreasing relationship of −0.4%/year (95% CI: −0.7 to 0.0) was found for meticillin resistance, reflecting widespread declines in meticillin-resistant S. aureus across Europe over the study period. ConclusionWe found evidence of a long-term effect of ambient minimum temperature on antibiotic resistance rate increases in Europe. Ambient temperature might considerably influence antibiotic resistance growth rates, and explain geographic differences observed in cross-sectional studies. Rising temperatures globally may hasten resistance spread, complicating mitigation efforts. METHODS: We introduced a methodology designed to automatically extract information from continuous-in-time vital sign data collected from bedside monitors to predict if a patient will experience a prolonged stay (length of stay) on mechanical ventilation, defined as >4 d, in a pediatric ICU. RESULTS: Continuous-in-time vital signs information and clinical history data were retrospectively collected for 284 ICU subjects from their first 24 h on mechanical ventilation from a medical-surgical pediatric ICU at Boston Children's Hospital. Multiple machine learning models were trained on multiple subsets of these subjects to predict the likelihood that each of these subjects would experience a long stay. We evaluated the predictive power of our models strictly on unseen hold-out validation sets of subjects. Our methodology achieved model performance of >83% (area under the curve) by using only vital sign information as input, and performances of 90% (area under the curve) by combining vital sign information with subjects' static clinical data readily available in electronic health records. We implemented this approach on 300 independently trained experiments with different choices of training and hold-out validation sets to ensure the consistency and robustness of our results in our study sample. The predictive power of our approach outperformed recent efforts that used deep learning to predict a similar task. CONCLUSIONS: Our proposed workflow may prove useful in the design of scalable approaches for real-time predictive systems in ICU environments, exploiting real-time vital sign information from bedside monitors. (ClinicalTrials.gov registration NCT02184208.) |
|
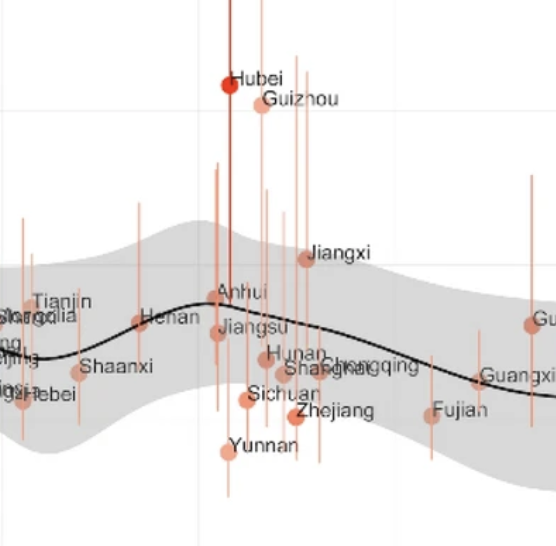
The Role of Environmental Factors on Transmission Rates of the COVID-19 Outbreak: An Initial Assessment in Two Spatial Scales
Poirier C, Luo W, Majumder MS, Liu D, Mandl K, Mooring T, Santillana M. Scientific Reports. 2020;10 :17002. Abstract
First identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) has affected over 16,800,000 people worldwide as of July 29, 2020 and was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization on March 11, 2020. Influenza studies have shown that influenza viruses survive longer on surfaces or in droplets in cold and dry air, thus increasing the likelihood of subsequent transmission. A similar hypothesis has been postulated for the transmission of COVID-19, the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2. It is important to propose methodologies to understand the effects of environmental factors on this ongoing outbreak to support decision-making pertaining to disease control. Here, we examine the spatial variability of the basic reproductive numbers of COVID-19 across provinces and cities in China and show that environmental variables alone cannot explain this variability. Our findings suggest that changes in weather (i.e., increase of temperature and humidity as spring and summer months arrive in the Northern Hemisphere) will not necessarily lead to declines in case counts without the implementation of drastic public health interventions. |
|
Using heterogeneous data to identify signatures of dengue outbreaks at fine spatio-temporal scales across Brazil
Castro LA, Generous N, Luo W, y Piontti AP, Martinez K, Gomes MFC, Osthus D, Fairchild G, Ziemann A, Vespignani A, et al. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 2021. Abstract
Dengue virus remains a significant public health challenge in Brazil, and seasonal preparation efforts are hindered by variable intra- and interseasonal dynamics. Here, we present a framework for characterizing weekly dengue activity at the Brazilian mesoregion level from 2010–2016 as time series properties that are relevant to forecasting efforts, focusing on outbreak shape, seasonal timing, and pairwise correlations in magnitude and onset. In addition, we use a combination of 18 satellite remote sensing imagery, weather, clinical, mobility, and census data streams and regression methods to identify a parsimonious set of covariates that explain each time series property. The models explained 54% of the variation in outbreak shape, 38% of seasonal onset, 34% of pairwise correlation in outbreak timing, and 11% of pairwise correlation in outbreak magnitude. Regions that have experienced longer periods of drought sensitivity, as captured by the “normalized burn ratio,” experienced less intense outbreaks, while regions with regular fluctuations in relative humidity had less regular seasonal outbreaks. Both the pairwise correlations in outbreak timing and outbreak trend between mesoresgions were best predicted by distance. Our analysis also revealed the presence of distinct geographic clusters where dengue properties tend to be spatially correlated. Forecasting models aimed at predicting the dynamics of dengue activity need to identify the most salient variables capable of contributing to accurate predictions. Our findings show that successful models may need to leverage distinct variables in different locations and be catered to a specific task, such as predicting outbreak magnitude or timing characteristics, to be useful. This advocates in favor of “adaptive models” rather than “one-size-fits-all” models. The results of this study can be applied to improving spatial hierarchical or target-focused forecasting models of dengue activity across Brazil. |
|
A dynamic, ensemble learning approach to forecast dengue fever epidemic years in Brazil using weather and population susceptibility cycles
McGough S, Kutz NJ, Clemente LC, Santillana M. Journal of the Royal Society Interface. 2021;18 (179) Abstract
Transmission of dengue fever depends on a complex interplay of human, climate and mosquito dynamics, which often change in time and space. It is well known that its disease dynamics are highly influenced by multiple factors including population susceptibility to infection as well as by microclimates: small-area climatic conditions which create environments favourable for the breeding and survival of mosquitoes. Here, we present a novel machine learning dengue forecasting approach, which, dynamically in time and space, identifies local patterns in weather and population susceptibility to make epidemic predictions at the city level in Brazil, months ahead of the occurrence of disease outbreaks. Weather-based predictions are improved when information on population susceptibility is incorporated, indicating that immunity is an important predictor neglected by most dengue forecast models. Given the generalizability of our methodology to any location or input data, it may prove valuable for public health decision-making aimed at mitigating the effects of seasonal dengue outbreaks in locations globally. |
|
Evaluating the performance of infectious disease forecasts: A comparison of climate-driven and seasonal dengue forecasts for Mexico
Johansson MA, Reich NG, Hota A, Brownstein JS, Santillana M. Scientific Reports. 2016;6 (33707). Abstract
Dengue viruses, which infect millions of people per year worldwide, cause large epidemics that strain healthcare systems. Despite diverse efforts to develop forecasting tools including autoregressive time series, climate-driven statistical and mechanistic biological models, little work has been done to understand the contribution of different components to improved prediction. We developed a framework to assess and compare dengue forecasts produced from different types of models and evaluated the performance of seasonal autoregressive models with and without climate variables for forecasting dengue incidence in Mexico. Climate data did not significantly improve the predictive power of seasonal autoregressive models. Short-term and seasonal autocorrelation were key to improving short-term and long-term forecasts, respectively. Seasonal autoregressive models captured a substantial amount of dengue variability, but better models are needed to improve dengue forecasting. This framework contributes to the sparse literature of infectious disease prediction model evaluation, using state-of-the-art validation techniques such as out-of-sample testing and comparison to an appropriate reference model. |